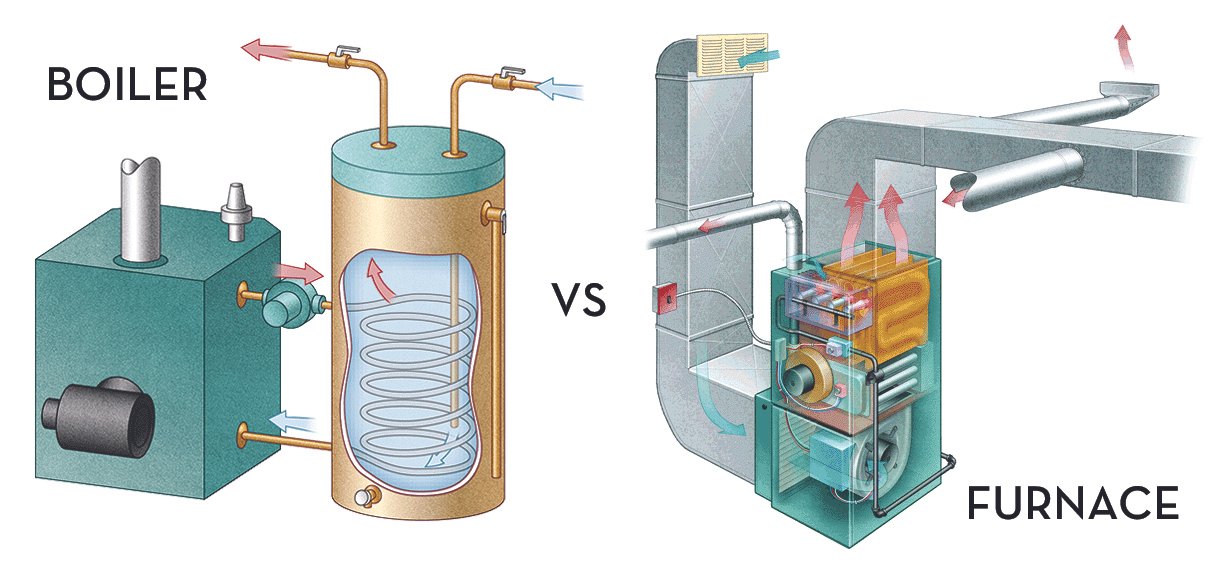
Boiler vs. Furnace: Understanding the Differences
When it comes to heating your home, boilers and furnaces are two popular choices that play a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. While both serve the same purpose of providing warmth, they operate in distinct ways. In this blog post, we will delve into the key differences between boilers and furnaces to help you make an informed decision when it's time to upgrade or replace your heating system.
Heating Mechanism:
Boiler: Boilers heat water to produce steam or hot water, which is then circulated through pipes or radiators to distribute heat throughout the home. The use of water as a heat transfer medium is a characteristic feature of boilers.
Furnace: Furnaces, on the other hand, generate heat by burning fuel, typically natural gas or oil. The heat produced warms air, which is then distributed through a system of ducts and vents. The warm air reaches various rooms in the house, providing consistent heating.
Distribution System:
Boiler: Boilers use pipes or radiators to distribute heat. The warm water or steam travels through pipes to reach radiators, baseboard heaters, or radiant floor systems, releasing heat into the surrounding space.
Furnace: Furnaces use a ductwork system to distribute warm air. The heated air is pushed through ducts and delivered to rooms through vents or registers. This forced air system allows for quick and efficient heating.
Energy Efficiency:
Boiler: Boilers are known for their energy efficiency, as water has a higher heat retention capacity than air. They often result in less heat loss during distribution, making them a cost-effective option in the long run.
Furnace: While modern furnaces have become more energy-efficient, they may experience some heat loss through the ductwork. Proper insulation and regular maintenance can help minimize this loss.
Maintenance and Lifespan:
Boiler: Boilers generally have a longer lifespan than furnaces. They require less frequent maintenance, but it's crucial to address any issues promptly to prevent damage to the system.
Furnace: Furnaces may have a shorter lifespan compared to boilers. Regular filter changes and maintenance are essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent breakdowns.
Cost Considerations:
Boiler: The initial cost of installing a boiler system can be higher than that of a furnace. However, the long-term energy savings and durability may offset the initial investment.
Furnace: Furnaces are often more affordable upfront, but the overall cost of operation, including energy bills and maintenance, should be considered over the system's lifespan.
Conclusion:
Choosing between a boiler and a furnace depends on various factors, including your heating needs, budget, and the layout of your home. Both systems have their advantages, and the decision should be based on what aligns best with your preferences and requirements. Whether you opt for the even warmth of a boiler or the quick, forced-air heat of a furnace, ensuring regular maintenance and efficient operation will keep your home comfortable throughout the colder months.